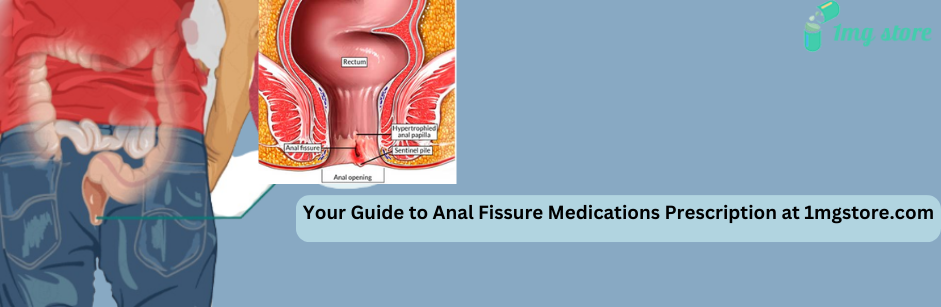
Anal fissure
-
Generic: Heparin SodiumEquivalent Brand: Liquaemin1 Tube$7.00
-
Generic: Lidocaine + NifedipineEquivalent Brand: Anobliss1 Tube$5.00
-
An anal fissure is a small tear or cut in the lining of the anus, which can cause pain and discomfort during bowel movements. While anal fissures are a common condition, they can be quite uncomfortable. Here are key aspects of anal fissures:
Causes:
- Straining During Bowel Movements: Hard or large stools can cause stretching and tearing of the anal lining during bowel movements.
- Constipation: Chronic constipation can lead to the passage of dry and hard stools, increasing the risk of fissures.
- Diarrhea: Prolonged or chronic diarrhea can irritate and damage the anal lining.
- Childbirth: Anal fissures can occur in women after childbirth, especially during vaginal delivery.
- Anal Trauma: Injury to the anal area, such as from anal intercourse or the insertion of foreign objects, can contribute to fissures.
Symptoms:
- Pain During Bowel Movements: Pain and discomfort, often described as a sharp or burning sensation, during and after bowel movements.
- Bright Red Blood: The presence of bright red blood on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl after a bowel movement.
- Itching: Itching or irritation around the anal area.
- Muscle Spasms (Anal Fissure Spasm): The anal sphincter muscles may go into spasm, causing additional pain.
Treatment and Management:
- Dietary Changes: Increasing fiber intake through fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can soften stools and promote regular bowel movements.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated helps maintain softer stools.
- Warm Sitz Baths: Soaking the anal area in warm water for 10-15 minutes several times a day can help relieve discomfort and promote healing.
- Topical Analgesics: Over-the-counter creams or ointments containing local anesthetics or topical steroids may be recommended for pain relief and reducing inflammation.
- Stool Softeners: These medications can help prevent constipation and promote softer stools.
- Prescription Medications: In some cases, medications like nitroglycerin ointment may be prescribed to relax the anal sphincter muscles.
- Botulinum Toxin Injection: In cases of persistent sphincter spasms, botulinum toxin (Botox) injections may be considered to relax the muscles.
- Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy: In cases where conservative measures are ineffective, a surgical procedure known as a lateral internal sphincterotomy may be performed to relax the anal sphincter.
Prevention:
- Maintaining Regular Bowel Movements: Avoiding prolonged periods of constipation or diarrhea helps prevent the development of anal fissures.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fiber and adequate hydration contribute to softer stools and easier bowel movements.
- Good Hygiene: Keeping the anal area clean and dry can help prevent irritation and reduce the risk of fissures.
- Avoid Straining: Straining during bowel movements should be minimized to reduce the pressure on the anal canal.
Anal fissures are usually treatable with conservative measures, but persistent or severe cases may require medical intervention. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment based on individual circumstances.