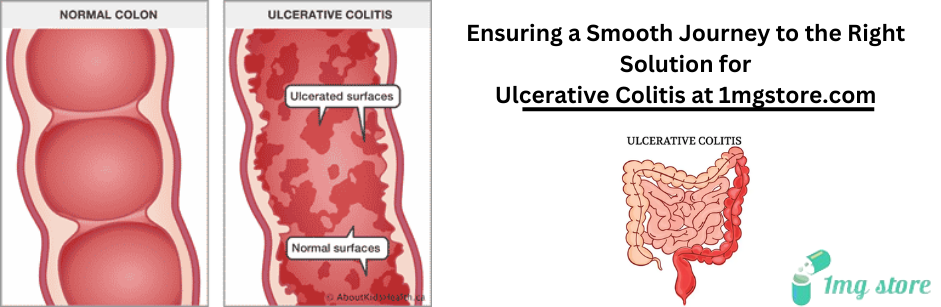
Ulcerative Colitis
-
Generic: MesalazineEquivalent Brand: Apriso30 Tablet/s$12.00
-
Generic: MesalamineEquivalent Brand: Canasa30 Tablet/s$26.00
-
Generic: MesalamineEquivalent Brand: Apriso30 Sachet/s$61.00
-
Generic: MesalamineEquivalent Brand: Canasa28 Unit/s$75.00
-
Generic: MesalazineEquivalent Brand: Apriso30 Tablet/s$42.00
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that primarily affects the colon and rectum. It is characterized by inflammation and ulcers in the lining of the large intestine, leading to various symptoms and potential complications. Here are key aspects of ulcerative colitis:
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Autoimmune Response: The exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to involve an abnormal immune response where the immune system mistakenly attacks the healthy cells of the digestive tract.
- Genetic Factors: Individuals with a family history of ulcerative colitis may have an increased risk.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors, such as certain infections or the composition of gut microbiota, may contribute to the development of ulcerative colitis.
Symptoms:
- Diarrhea: Frequent, loose stools with blood or pus.
- Abdominal Pain and Cramping: Persistent abdominal discomfort, cramping, and pain.
- Rectal Bleeding: Blood in the stool or visible in the toilet bowl.
- Urgency and Inability to Control Bowel Movements: The feeling of needing to urgently pass stools and difficulty controlling bowel movements.
- Fatigue: Chronic inflammation and symptoms can lead to fatigue.
- Weight Loss: Loss of appetite and weight loss may occur.
- Fever: In some cases, fever may be present during flare-ups.
Types of Ulcerative Colitis:
- Ulcerative Proctitis: Inflammation is limited to the rectum.
- Proctosigmoiditis: Inflammation extends to the sigmoid colon.
- Left-sided Colitis: Inflammation extends to the descending colon.
- Pancolitis: Inflammation affects the entire colon.
- Fulminant Colitis: Severe, potentially life-threatening inflammation involving the entire colon.
Diagnosis:
- Colonoscopy: A procedure to examine the colon and rectum using a flexible tube with a camera.
- Biopsy: Small tissue samples may be taken during a colonoscopy to confirm the diagnosis.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to check for inflammation, anemia, and other markers.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays or imaging studies may be used to assess the extent of inflammation.
Treatment and Management:
- Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Medications such as aminosalicylates or corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation.
- Immunosuppressants: Drugs that suppress the immune system, such as azathioprine or methotrexate, may be prescribed.
- Biologics: Biological therapies that target specific immune pathways may be used in certain cases.
- Anti-diarrheal Medications: Medications to control diarrhea may be recommended.
- Nutritional Support: In some cases, nutritional therapy or dietary changes may be part of the management plan.
- Surgery: In severe cases or if complications arise, surgical removal of the colon (colectomy) may be necessary.
Complications:
- Colon Cancer Risk: Individuals with long-standing ulcerative colitis have an increased risk of developing colon cancer.
- Toxic Megacolon: Severe inflammation can lead to a dangerous condition called toxic megacolon, requiring emergency medical attention.
- Perforation of the Colon: In rare cases, the inflammation can lead to perforation of the colon.
Lifestyle and Coping:
- Stress Management: Stress management techniques can help in symptom control.
- Dietary Modifications: Some individuals find relief with specific dietary changes, but this can vary.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are important for monitoring symptoms and adjusting treatment as needed.
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management. With proper medical care, individuals with ulcerative colitis can lead full and productive lives. A personalized treatment plan, close communication with healthcare providers, and a supportive lifestyle can contribute to effective management of the condition.